Sirena Deep
12°3.924′N 144°34.868′E / 12.065400°N 144.581133°E

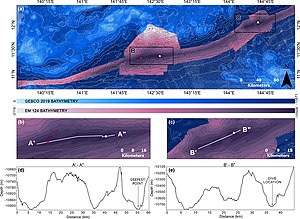
(a) Mariana Trench multibeam bathymetry data gridded at 75 m acquired on‐board the DSSV Pressure Drop overtop the GEBCO 2019 source grid (as shown in Figure 1) and the complete GEBCO 2019 grid with hillshade. EM 124 black contours at 500 m intervals, GEBCO 2019 grey contours at 1,000 m intervals. The white circle indicates the deepest point and submersible dive location, the white triangle indicates the submersible dive location from Sirena Deep, the red spot was the deepest point derived by van Haren et al., (2017).
(b) Challenger Deep.
(c) Sirena Deep.
Bathymetric cross sections A’–A” and B’–B” over Challenger Deep and Sirena Deep displayed in (d) and (e), respectively.
The Sirena Deep, originally named the HMRG Deep, was discovered in 1997[1][2] by a team of scientists from Hawaii.[2] Its directly measured depth of 10,714 m (35,151 ft) is third only to the Challenger Deep and Horizon Deep, currently the deepest known directly measured places in the ocean.[3][4][5] It lies along the Mariana Trench, 200 kilometers to the east of the Challenger Deep and 145 km south of Guam.[1][2]
Formation
[edit]The Sirena Deep was most probably formed, not through transform fault motion as previously thought, but through a north-south convergence of the Caroline plate and the Pacific plate, in which the Caroline plate is subducting.[3] A group of scientists have hypothesized that the great depth of the Mariana Trench, the Challenger Deep, and the Sirena Deep is due to a tear in the subducting Caroline plate, causing deformation of the Pacific plate above.[3] This tear would be located to the south of Guam, the same location of the deepest portion of the Mariana Trench.[3] The tear would lead to unusual regional tectonics, another possible reason for the extreme depth.[3] Scientists were alerted to the presence of the tear by the depth of strike-slip earthquakes, which were occurring too deep for them to be in the overriding plate.
The Sirena Deep lies at the intersection of the East Santa Rosa Bank Fault and a trench axis south of Guam.[3]
History
[edit]Discovery
[edit]In 1997, the Hawaiʻi Mapping Research Group (HMRG) conducted a detailed sonar survey of the seafloor around Guam, discovering what is believed to be the second or third deepest[4][5][6] location in the world's oceans; its existence was confirmed in 2001 and it was temporarily named HMRG Deep.[2][6] In the same research mission, scientists found previously undiscovered faults, landslides, and mud volcanoes.[2]
The data that confirmed the discovery were collected using the HAWAII MR1 mapping system. This mapping system has the ability to record both bathymetry and sidescan data at the same time. The two vessels that this system was used on were RIV Moana Wave in 1997 and RIV Melville in 2001.[3]
Renaming
[edit]After a competition was held in 2009 by Patricia Fryer, her doctoral student Sam Hulme, and Linda Tatreau to rename the HMRG Deep,[6] the new name of Sirena Deep was chosen. Students from Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands ages 18 and younger competed,[6][7] with the winning name being suggested by Jermaine Sanders (aged 16) and John Meno (aged 14). The new name references the Guam folk-tale of Sirena, a young girl turned into half fish because of her disobedience.[8] The new name will now appear on geologic and bathymetric maps.
Crewed descent
[edit]
On 7 May 2019 Victor Vescovo (Pilot) and Alan Jamieson (Chief Scientist) made the first crewed descent to the bottom of the Sirena Deep in the Deep-Submergence Vehicle Limiting Factor (a Triton 36000/2 model submersible) and measured a depth of 10,714 m (35,151 ft) ±10 m (33 ft) by direct CTD pressure measurements. This descent occurred just after descending four times to the bottom of the nearby Challenger Deep. Work focused on geological, biological and video survey and collection in the Mariana Trench basin. They spent 176 minutes on the bottom of the Sirena Deep and the deepest piece of mantle rock ever recovered from the surface of the western slope of the Mariana Trench was collected.[9][10] The Mariana Trench and the operating area was surveyed by the support ship, the Deep Submersible Support Vessel DSSV Pressure Drop, with a Kongsberg SIMRAD EM124 multibeam echosounder system. The gathered data will be donated to the GEBCO Seabed 2030 initiative.[11][12] The dive was part of the Five Deeps Expedition. The objective of this expedition was to thoroughly map and visit the deepest points of all five of the world's oceans by the end of September 2019, which was achieved.[13][14]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Sukola, Tiffany. "Last chance to get 'your name' in the books". Retrieved 15 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d e Whitehouse, David (12 July 2003). "Sea floor survey reveals deep hole". BBC News. Retrieved 9 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g Patricia Fryer; Nathan Becker; Bruce Appelgate; Fernando Martinez; Margo Edwards; Gerard Fryer (2003). "Why is the Challenger Deep So Deep?". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 211 (3–4) (published 29 May 2003): 259–269. Bibcode:2003E&PSL.211..259F. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00202-4.
- ^ a b Wright, Dawn J., Sherman H. Bloomer, Christopher J. MacLeod, Brian Taylor, & Andrew M. Goodlife (2001). "Bathymetry of the Tonga Trench and Forearc: a map series" (PDF). Marine Geophysical Researches. 21 (5): 489–511. Bibcode:2000MarGR..21..489W. doi:10.1023/A:1026514914220. S2CID 6072675. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2009. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Steve Nicholls (producer/writer), Victoria Coules (writer), Peter Brownlee (editor) (9 August 2009). Drain the Ocean (Documentary). National Geographic. Archived from the original on 13 July 2009.
- ^ a b c d Flores, J.T. "Guam gets to name trench spot". Retrieved 15 August 2009.
- ^ "DEEPSEA CHALLENGE - Marianas Trench Marine National Monument". 24 March 2012. Retrieved 21 September 2016.
- ^ Ramirez, Toni (23 December 2020). "Folktale: Sirena". Guampedia. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- ^ Deepest Ever Submarine Dive Made by Five Deeps Expedition
- ^ "Deepest Submarine Dive in History, Five Deeps Expedition Conquers Challenger Deep" (PDF). fivedeeps.com. Retrieved 13 May 2019.
- ^ "The Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project". Archived from the original on 16 June 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2019.
- ^ "Major partnership announced between The Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project and The Five Deeps Expedition". gebco.net. 11 March 2019. Archived from the original on 19 June 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2019.
- ^ "Home". fivedeeps.com. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ Bongiovanni, Cassandra; Stewart, Heather A.; Jamieson, Alan J. (2022). "High-resolution multibeam sonar bathymetry of the deepest place in each ocean". Geoscience Data Journal. 9. Royal Meteorological Society: 108–123. doi:10.1002/gdj3.122. S2CID 235548940.
External links
[edit]- former HMRG homepage, under the University of Hawaii
- HIGP homepage (Hawaiʻi Institute of Geophysics and Planetology), also under the University of Hawaii
